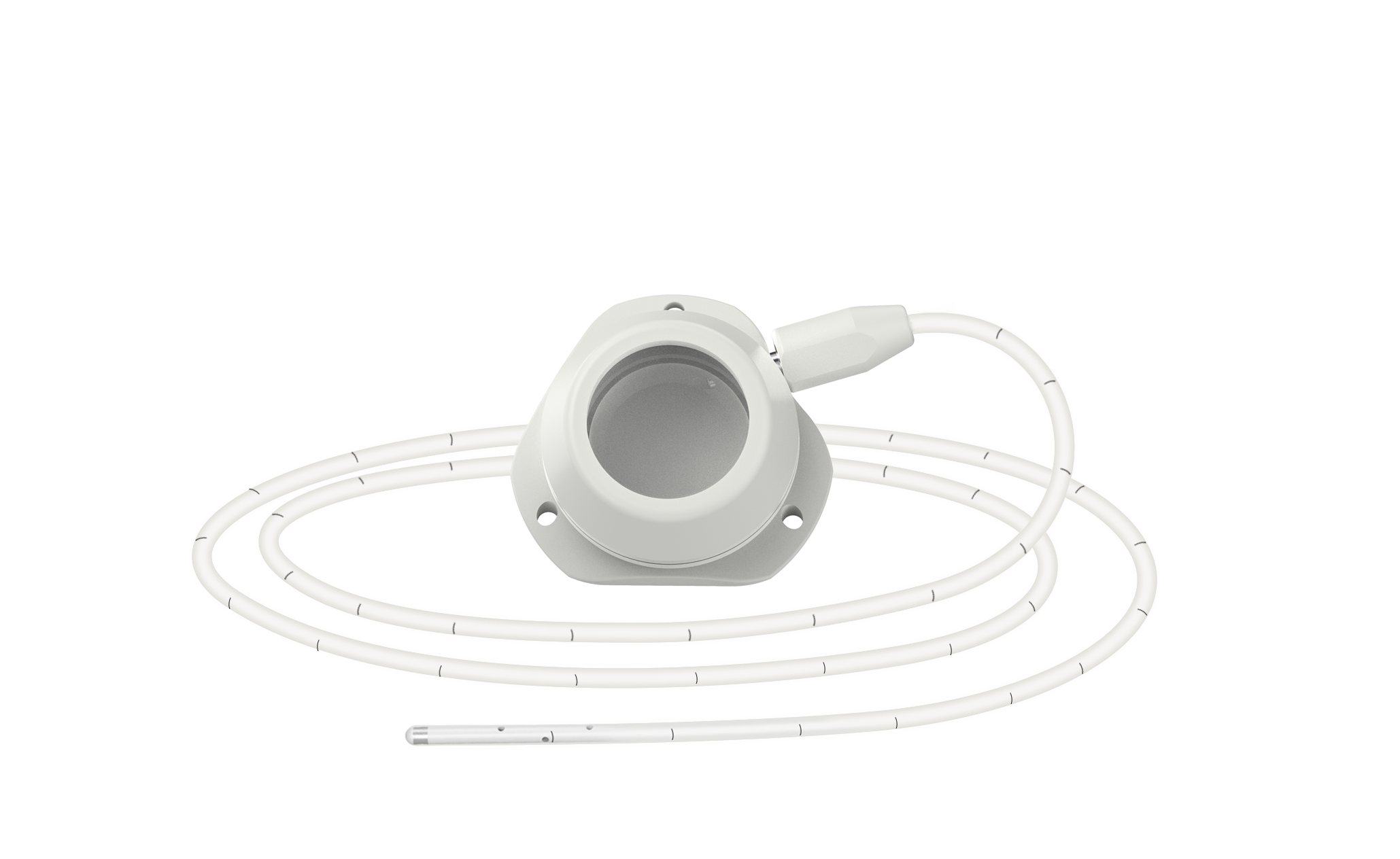
Implantable Access Port
From: Products Date: 2025-09-01 10:43INTRATHECAL ANALGESIA
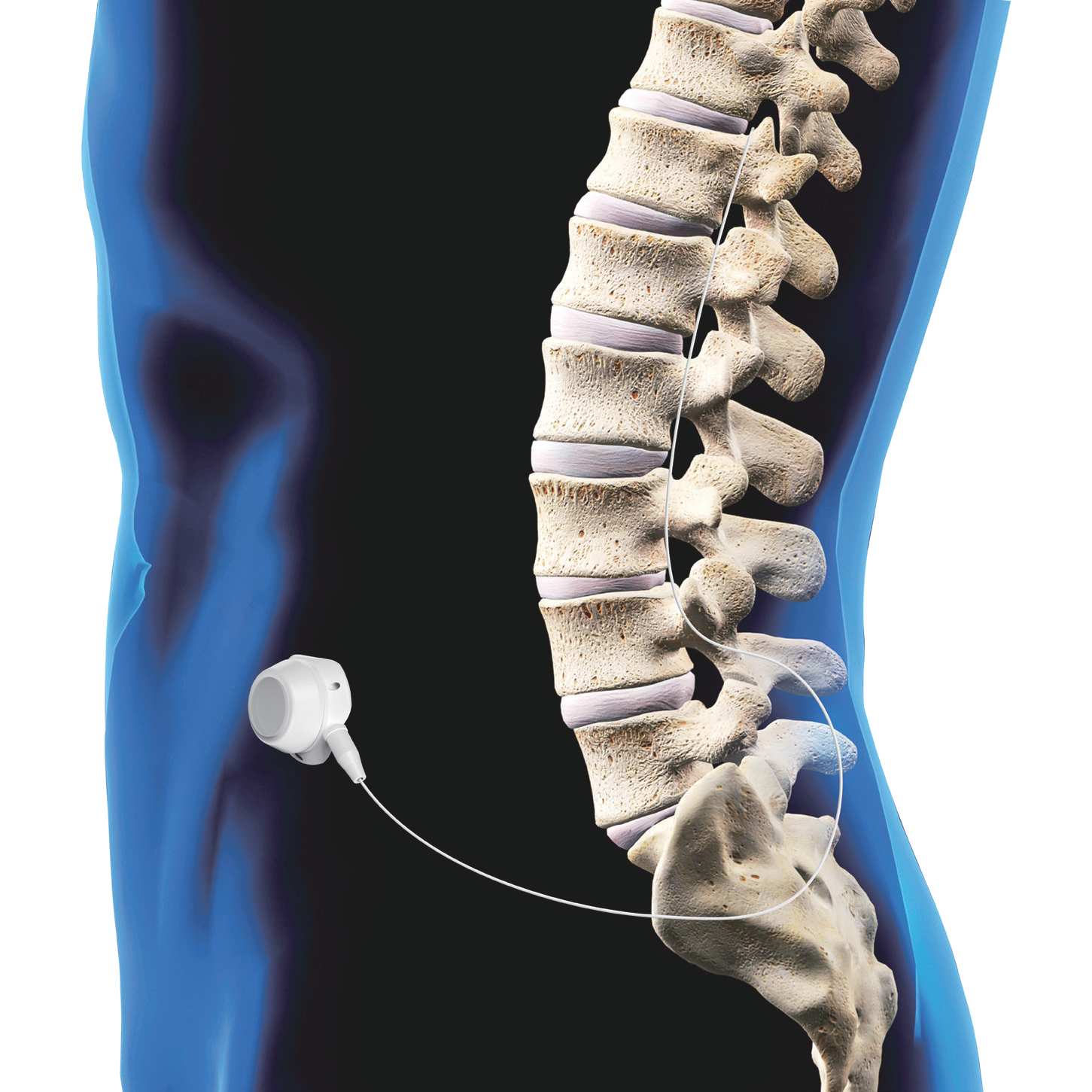
Intrathecal analgesia involves implanting a catheter into the subarachnoid space at the vertebral segment corresponding to the painful site through a puncture procedure under local anesthesia. The injection port is placed subcutaneously and connected to the catheter. Analgesics can be delivered to the subarachnoid space via the injection port for targeted drug administration, thereby achieving the goal of pain relief.
The analgesic efficacy of intrathecal morphine is approximately 100 times that of intravenous administration and about 300 times that of oral administration

![]()
PRODUCT FEATURES
High-strength catheter
New TPU material
Double-layer?catheter for fracture resistance
Compatible with?Implanted Drug Delivery System
85cm length, trim to fit
Fully graduated markings
Extremely long service life
Material suitable for long-term implantation
Up to?1000?doses
Angential outlet
Facilitates flushing and cleaning?of the entire wound?chamber
Uniform?drug delivery,?Rapid onset of action
6-port drug delivery
360°three-dimensional distribution
Clear imaging,?Precise positioning
Catheter, access port, and catheter holder are CT-detectable
Embedded positioning ring at catheter tip

